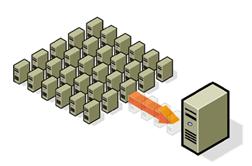
 If there is anything that the recent recession and the current debt crisis of the United States and Europe have taught us, it is that businesses must save every penny that they can in any way possible.Server virtualisation technology is an advancement which allows businesses, especially those on small budgets, the ability to have the same protection and management of data as enterprise level businesses for a fraction of the cost.Server virtualisation technology is technically placing the data streams of different clients inside of the same physical server while segregating the data streams so as to simulate a dedicated server experience for each of the clients in the physical server. Since the same physical server is being used, each client does not have to pay for the resource of a dedicated server. However, because the server is virtual, each client receives the same resources as they would on a dedicated server.On a virtual server, each client can download different third party apps and even different operating systems without disturbing the other clients on the server. Security is also increased as data leaks in the data stream of one client also do not affect the other clients.
If there is anything that the recent recession and the current debt crisis of the United States and Europe have taught us, it is that businesses must save every penny that they can in any way possible.Server virtualisation technology is an advancement which allows businesses, especially those on small budgets, the ability to have the same protection and management of data as enterprise level businesses for a fraction of the cost.Server virtualisation technology is technically placing the data streams of different clients inside of the same physical server while segregating the data streams so as to simulate a dedicated server experience for each of the clients in the physical server. Since the same physical server is being used, each client does not have to pay for the resource of a dedicated server. However, because the server is virtual, each client receives the same resources as they would on a dedicated server.On a virtual server, each client can download different third party apps and even different operating systems without disturbing the other clients on the server. Security is also increased as data leaks in the data stream of one client also do not affect the other clients.As to the resources that each individual client receives on a virtual server, they may not quite match the resources of a dedicated server, but they are usually enough for all but the largest enterprise level business establishments. Virtual technology also allows the resources of the server to be allocated to the business as they are needed, which saves a business from having to pay too early for services that they do not use or underestimate the services that they do need.
Virtual servers can be managed or unmanaged services. In a managed service, the virtual server host is responsible for all of the maintenance to the server. In unmanaged service, the client is responsible for the maintenance. This is usually only a wise course of action if a business has the manpower and the resources to take care of a server themselves. However, since the server itself is rented from the server hosting company, it is usually the best policy to let the server host take care of it, as they are the ones who actually own the server.
Businesses who are set to grow may also want to invest in an unmetered line. In the unmetered line of a virtual server the amount of data which is able to be streamed through the server has no limit, which will allow for the most growth possible for a business with traffic spikes and constant rises in traffic.
Certain types of software do not run well in virtual environments – this is really the only weakness of server virtualisation technology.
