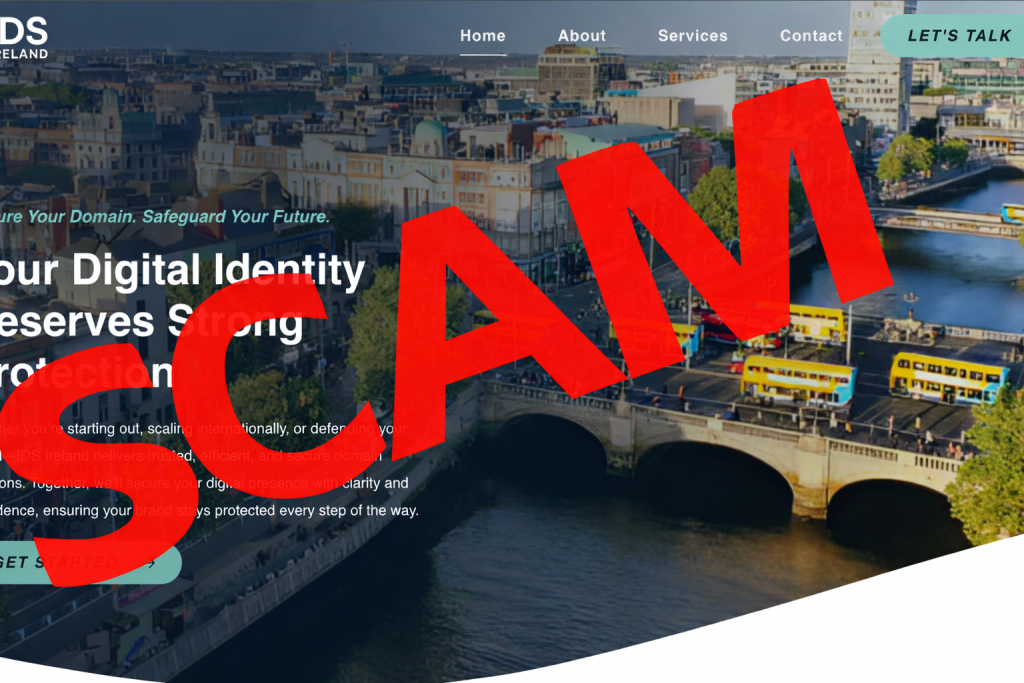
Have you recently received an invoice that looks official for a domain name renewal or online service? It might come from a company you don’t recognise, like “IDS Ireland” (idsireland.com). Be warned – this is a sophisticated scam designed to trick busy business owners into paying for services that don’t exist.
At CK Computer Solutions, we’re seeing a rise in these fake invoices and want to ensure our clients and the wider business community are protected. Here’s what you need to know and what to do if you receive one.
Who Are the Scammers at idsireland.com?
The website idsireland.com presents itself as a legitimate business offering domain registration, SEO services, and online directory listings. However, this is a front. Their primary business model is sending out high volumes of convincing, yet entirely fraudulent, invoices.
They prey on the fact that many businesses handle dozens of invoices every month. Their goal is to slip their fake invoice past a busy accounts department and get paid before anyone realises it’s a scam.
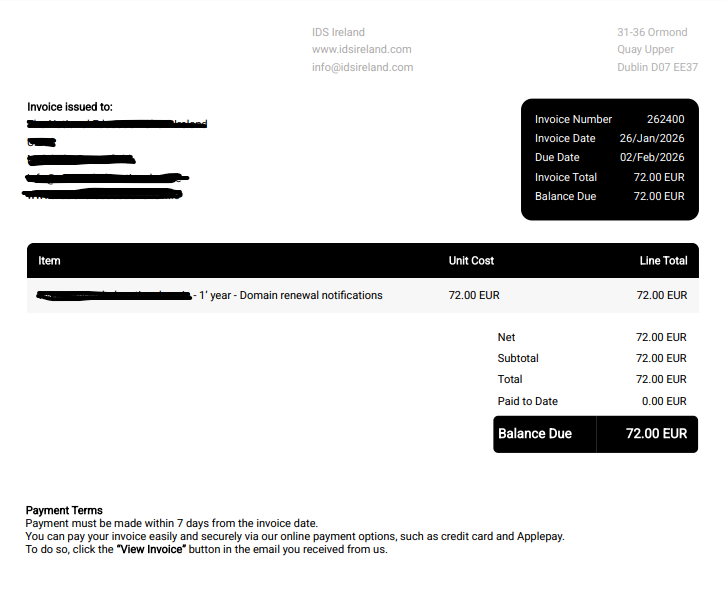
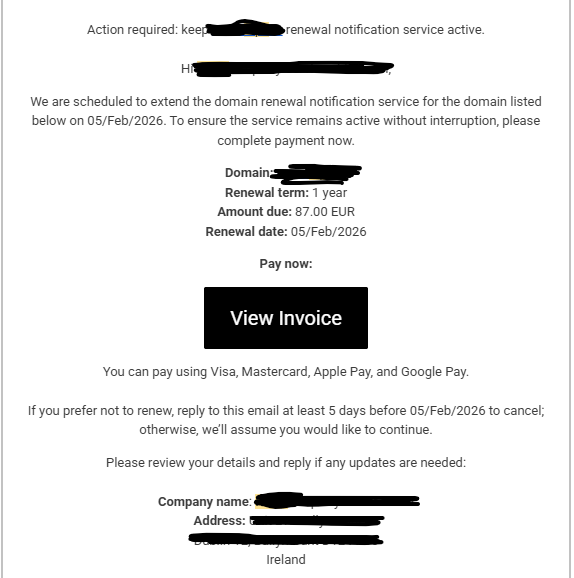
The Deceptive Art of the Fake PDF Invoice
What makes this scam particularly effective is how professional the invoice looks. This isn’t a poorly written email from a prince in a foreign land.
- It’s a PDF: An attached PDF file immediately lends an air of legitimacy. It looks like a “real” document that you might print or file away.
- Official Branding: The PDF will often have a logo, your business name, an invoice number, and a due date.
- Plausible Amounts: The amounts they request are often small enough (e.g., €50, €95, €200) not to raise immediate red flags. A busy person might just see “domain renewal” and approve the payment without a second thought.
It’s incredibly easy to fall for it. The scammers are counting on you being too busy to double-check every single service provider.
Red Flags to Spot a Fake Invoice
Always be suspicious of an invoice if:
- The sender is unfamiliar: Have you ever done business with “IDS Ireland” or the company named on the invoice?
- The service description is vague: It might say “Domain Renewal” or “SEO Service” but won’t specify the exact domain name or website it’s for.
- There’s a sense of urgency: The invoice may threaten that your service will be “suspended” or “cancelled” if you don’t pay immediately.
- The payment details are strange: They may ask for a bank transfer to an unusual account or use a payment processor you don’t recognise.
What to Do If You Receive a Suspicious Invoice: A Step-by-Step Guide
Receiving one of these can be unsettling, but the correct response is simple and crucial.
STEP 1: DO NOT PAY! This is the most important rule. Do not click any payment links, do not make a bank transfer, and do not provide any credit card details. Paying the invoice will not only lose you money but also confirm to the scammers that your email address is active, likely leading to more scam attempts.
STEP 2: DO NOT CLICK OR ENGAGE Do not click any links in the email or the PDF. Do not reply to the email. Do not click “Unsubscribe”. Clicking links can lead to malicious websites, and replying confirms your email address is active.
STEP 3: INDEPENDENTLY VERIFY THE INVOICE This is where you can fight back. If you are even slightly unsure about an invoice for a domain, hosting, or any IT service, your first port of call should be your trusted IT provider.
Contact CK Computer Solutions immediately to verify if the email is genuine or not.
When you contact us, we can quickly check our records and confirm whether we have issued the invoice or if the service is legitimate. We will always give you a clear, honest answer.
IMPORTANT: Do not use any contact information, phone numbers, or websites listed on the suspicious invoice. Find our contact details through a trusted source, like our official website or a previous email you know is genuine.
STEP 4: DELETE AND REPORT Once CK Computer Solutions (or your trusted provider) has confirmed the invoice is a fake, delete the email and mark it as “Phishing” or “Spam” in your email client. This helps your email provider filter out future attempts.
Stay Vigilant and Stay Protected
Scammers like those behind idsireland.com are always looking for new ways to deceive honest businesses. The best defence is a healthy dose of skepticism and a simple verification process.
Remember the golden rule: When in doubt, check it out.
Never make a payment for a service you can’t 100% verify. If you have any concerns about an invoice you’ve received, please do not hesitate to get in touch with CK Computer Solutions. We are here to help keep your business safe and secure.
Share this post with your colleagues and business associates to help spread the word and stop these scammers in their tracks.


