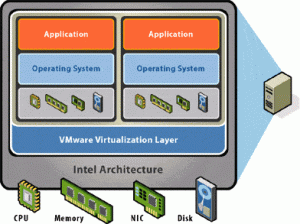
 While the use of virtual servers has gained a lot of popularity in the recent past, the concept is not as new as many people tend to assume. The history of server virtualisation can be traced as far back as the 1960s, when companies still used mini and mainframes. IBM wanted to run some simple processes that caused conflict when operated from one computer. At the same time, it was too expensive to have independent computers dedicated to the tasks. So they found a way of using software to partition one server to function as several independent servers.However, people gradually pushed the method to the background as technological advancements led to the production of smaller and cheaper computers.The use of many computers came with its own challenges though. The computers required an extensive cooling system, effectively pushing up the operating costs. On the other hand, the computers were greatly underutilised. People started taking server virtualisation seriously once more.Virtual servers provide several great benefits, including:CostServer virtualisation is significantly cheaper than using dedicated servers that are entirely meant for individual businesses. Several businesses share the same server but it is partitioned such that all users get hardware resources dedicated to their own uses. The method is especially ideal for business Web sites that attract five thousand or more views per day. Such businesses have too much demands for shared hosting to handle while using dedicated servers would be unnecessarily costly. Irrespective of how busy any day may be, the businesses are still assured of good performance.Flexibility
While the use of virtual servers has gained a lot of popularity in the recent past, the concept is not as new as many people tend to assume. The history of server virtualisation can be traced as far back as the 1960s, when companies still used mini and mainframes. IBM wanted to run some simple processes that caused conflict when operated from one computer. At the same time, it was too expensive to have independent computers dedicated to the tasks. So they found a way of using software to partition one server to function as several independent servers.However, people gradually pushed the method to the background as technological advancements led to the production of smaller and cheaper computers.The use of many computers came with its own challenges though. The computers required an extensive cooling system, effectively pushing up the operating costs. On the other hand, the computers were greatly underutilised. People started taking server virtualisation seriously once more.Virtual servers provide several great benefits, including:CostServer virtualisation is significantly cheaper than using dedicated servers that are entirely meant for individual businesses. Several businesses share the same server but it is partitioned such that all users get hardware resources dedicated to their own uses. The method is especially ideal for business Web sites that attract five thousand or more views per day. Such businesses have too much demands for shared hosting to handle while using dedicated servers would be unnecessarily costly. Irrespective of how busy any day may be, the businesses are still assured of good performance.FlexibilityBusinesses using virtual servers have the opportunity to choose their preferred operating systems as well as other programs.
They also have root access, which means they are not restricted to installing their server environments through their respective Web hosts. They fully control their own server environments and can install a wide variety of applications.
Better Availability
Server virtualisation allows live migration, whereby the virtual servers are moved to a different physical server to ensure continued availability during such things as maintenance. Therefore, businesses will not have their Web sites shut down, which interferes with their operations.
While server virtualisation undoubtedly has great benefits, it also has its own drawbacks.
Scalability
Businesses will create more demand on the virtual servers as they expand, leading them to use more resources at the expense of others. If the system is not designed with scalability in mind, the situation can be tricky. Businesses must consider this possibility in advance.
New Skills
Although having root access gives businesses more flexibility, it also has its own challenges. For example, the businesses will be responsible for their own setups, which requires relevant skills. However, server virtualisation is a good option for many businesses.
